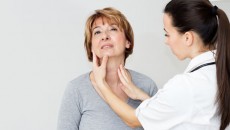
Clinical Definition
The thyroid is a small, soft gland inferior to the larynx in the anterior of the neck. The tissue of the gland is comprised of parafollicular and follicular cells. The thyroid secretes several hormones including triiodothyronine and thyroxin, which regulates metabolic rate. Diseases of the thyroid may develop if excess or insufficient hormone levels are produced by the gland.
In Our Own Words
The thyroid is a vital gland in the neck that secretes hormones that regulate metabolism (T3 and T4) and calcium levels (calcitonin). It is located in the front of the neck just below the Adam’s apple. One of the main functions of the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) is to increase our metabolic rate, revving up the breakdown of food and other energy supplies to meet increased demands. Associated signs are increased body temperature, faster heartbeat, and fast reflexes. Too much thyroid hormone results in hyperthyroidism. Not enough thyroid hormone results in hypothyroidism.