Monitoring Your Own Blood Sugar Levels
For those who have diabetes, healthy lifestyle management is vital to successfully living with the disease. A major part of that management is monitoring blood glucose (a.k.a., blood sugar) levels. These levels are checked every time you visit your doctor using an A1C test. This test, however, only gives your doctor an overall average of what your levels have been for the previous three months. While helpful, this information doesn’t provide an accurate picture of how your levels may be fluctuating from day-to-day.
Persistently fluctuating levels can cause quite a bit of cellular damage. The only way to truly know how much variance you experience in your levels on an everyday basis is to check your blood glucose on your own. Frequent blood sugar checks also help you see how any lifestyle changes that you’ve implemented are affecting your levels, and to see how you’re responding to your current diabetes medications.
Thus, understanding how to check your levels on your own is vital to living day-to-day with diabetes. If your doctor has just recently recommended that you begin this practice, the thought of actually doing so may seem rather daunting. Yet a few simple explanations and a little bit of experience is typically all that’s needed in order for you to start to feel comfortable doing these checks on your own.
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Testing Requirements
First, you need to know exactly how often you should check your levels and what times of the day are best for getting certain readings. This knowledge comes from an understanding of the specific type of diabetes from which you suffer and how certain conditions and practices may influence your testing frequency.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, your doctor will most likely recommend that you test yourself at least three times per day. Your testing frequency may need to be increased if you are ill or having recently changed your medication. The best times to test are before and after a large meal or an exercise session, before bed, and possibly during the night. If you suffer from type 2 diabetes, you may need to only test yourself once a day (that frequency may increase depending upon the amount of insulin you’re taking). Usually, the best time to test is immediately before eating a large meal after having fasted for at least eight hours.
It’s also recommended that you check your blood glucose if you start feeling the onset of hypoglycemia, regardless of the type of diabetes that you suffer from. You may also not need to test as frequently if you’re attempting to manage your diabetes through diet and exercise alone.
How to Perform a Check
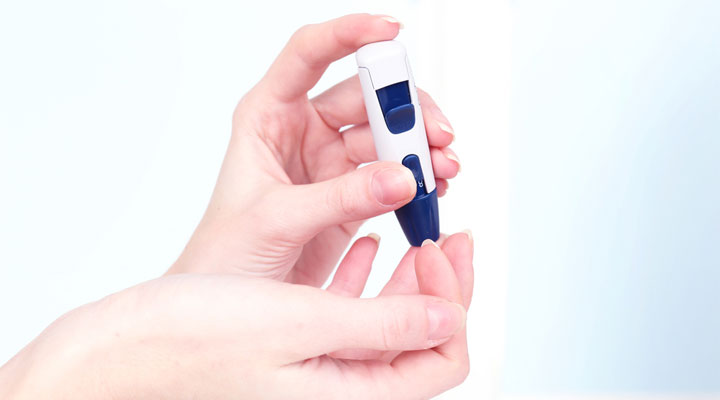
When it comes to actually performing the check, these are the steps you should follow:
- Wash your hands thoroughly. The most commonly recommended area of the body to perform a check is on the fingertip, as levels from samples drawn from there come nearest to those taken in a laboratory setting. Any bit of sugar on your fingertips can throw off your reading.
- Place a test strip into your meter. Enzymes in the test strip react with your blood to produce a glucose oxidase reaction. The meter measures this reaction to give you your reading.
- Prick your fingertip with the lancet. Only a small drop of blood is needed to generate a reading.
- Transfer the blood to the test strip, and then insert the strip into the meter.
What Your Readings Mean
Results take anywhere from three to 30 seconds to be displayed. Measurements are indicated in milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). Your target range should be from 70 to 130 mg/dL prior to eating and 90 to 150 m/dL prior to sleeping. Optimal readings after eating should be below 180 mg/dL within two hours.
Knowing how to correctly check your own blood glucose levels and understanding the results of those checks will have a drastic impact on the effectiveness of your diabetes management. With proper management comes the increased possibility of you being able to enjoy a long, healthy life.