Discover why painless may be the way to go with monitoring sugar levels.
Since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first prickless glucose monitor in 2017, the ability to manage diabetes more conveniently and effectively is changing how people monitor diabetes.
Diabetes patients rely on knowing their glucose levels for their day-to-day health, but how they go about measuring the glucose has been relatively unchanged before the prickless glucose monitor came to market.
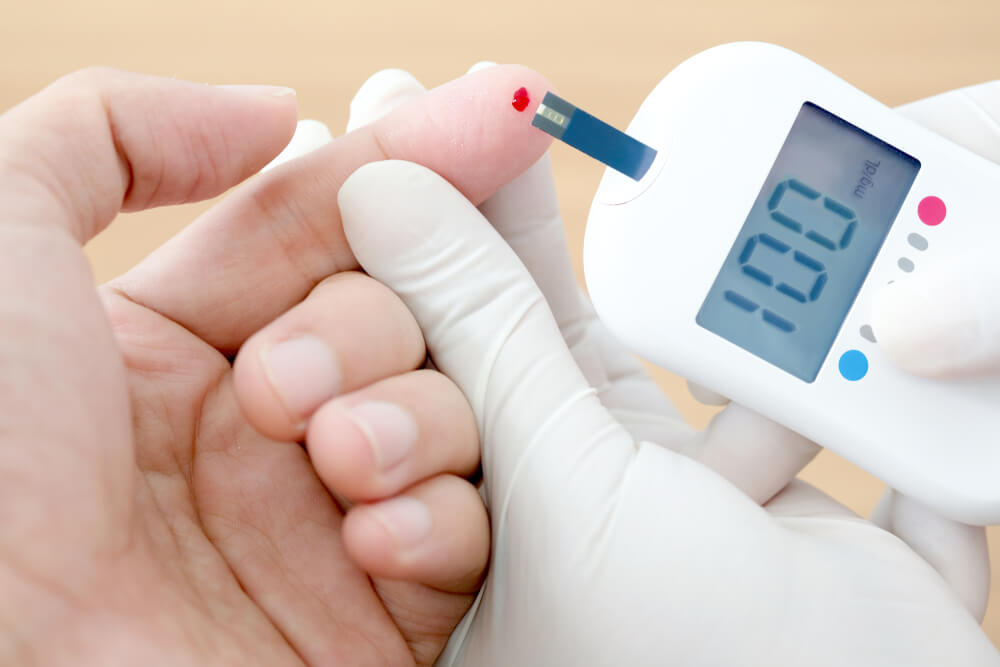
Insulin has been around for nearly 100 years, but the process involved with day-to-day management can be painful and infrequent. The most common form to measure glucose levels is still through a prick of the finger to draw blood and then measure it. If a patient decides to forego their finger being pricked, there are now options on the market for a bloodless glucose meter.
The first prickless glucose monitor approved by the FDA was the FreeStyle Libre Flash Glucose Monitoring System, which allowed adult patients to decide their diabetes treatment options without the use of taking a blood sample. By avoiding the need to prick a finger and draw blood, the prickless glucose monitor allows users to monitor their sugar levels more conveniently and without the pain of drawing blood.
Click here to find type 2 diabetes diet recommendations.
Benefits to Using a Bloodless Glucose Meter
In addition to less pain and no blood drawn, using a bloodless glucose meter permits you to measure your sugar levels by using a sensor wire placed under the skin to monitor blood sugar levels. The prickless glucose monitor is able to do this by measuring the glucose levels in the body’s fat vs. the body’s bloodstream.
When using the bloodless glucose meter, the data is tracked by the healthcare provider who can use the data to make helpful diabetes recommendations including adjustments to medicines.
A glucose meter without blood involved also allows for more measures throughout the day in order to stay on top of your sugar levels with the convenience of a handheld device. Then a diabetic can quickly determine if they have hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
With more ability to frequently monitor glucose levels, patients can develop a better understanding of the highs and lows of their glucose levels to ensure they stay on the correct path when it comes to diabetes management and the medication involved.
The data from the handheld device can also be shared with the patient’s doctor to help look for patterns in blood sugar to see if increases or decreases are related to stress, activity, medicine, and more.
With cost, access, and carrying around supplies among issues why some patients skip routine glucose level monitors, having a glucose meter without blood drawn can help alleviate determents while improving awareness of the disease.
Learn more on how to manage type 2 diabetes by clicking here.
Future of a Glucose Meter Without Blood Taken
Along with the recent approval of the bloodless glucose meter by the FDA, there are other glucose meters without blood options being tested. A new tattoo sensor works as a temporary tattoo with sensors that use a small electrical current to measure the glucose levels.
While not yet approved by the FDA, this is yet another form of a glucose meter without blood which will be becoming more prevalent in an effort to help diabetics better learn how to manage their diabetes on a day-to-day basis.
Before using a bloodless glucose meter, please consult your doctor on which monitoring device is best suited for you.
Learn more about glucose monitors at www.BetterHealthKare.com